AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: Understanding the Key Differences and Real-World Impact
Explore the nuances between AI Agents and Agentic AI, their real-world applications, and the implications for the future. Learn how these two powerful AI paradigms are shaping industries and our daily lives.
Artificial intelligence is rapidly evolving, and along with it, so is the terminology. You may have encountered the terms “AI Agents” and “Agentic AI” – while both relate to intelligent systems, they represent fundamentally different approaches to AI. This post clarifies these concepts, exploring their unique capabilities, applications, and implications.
What Are AI Agents and Agentic AI?
Let’s start with the core definitions.
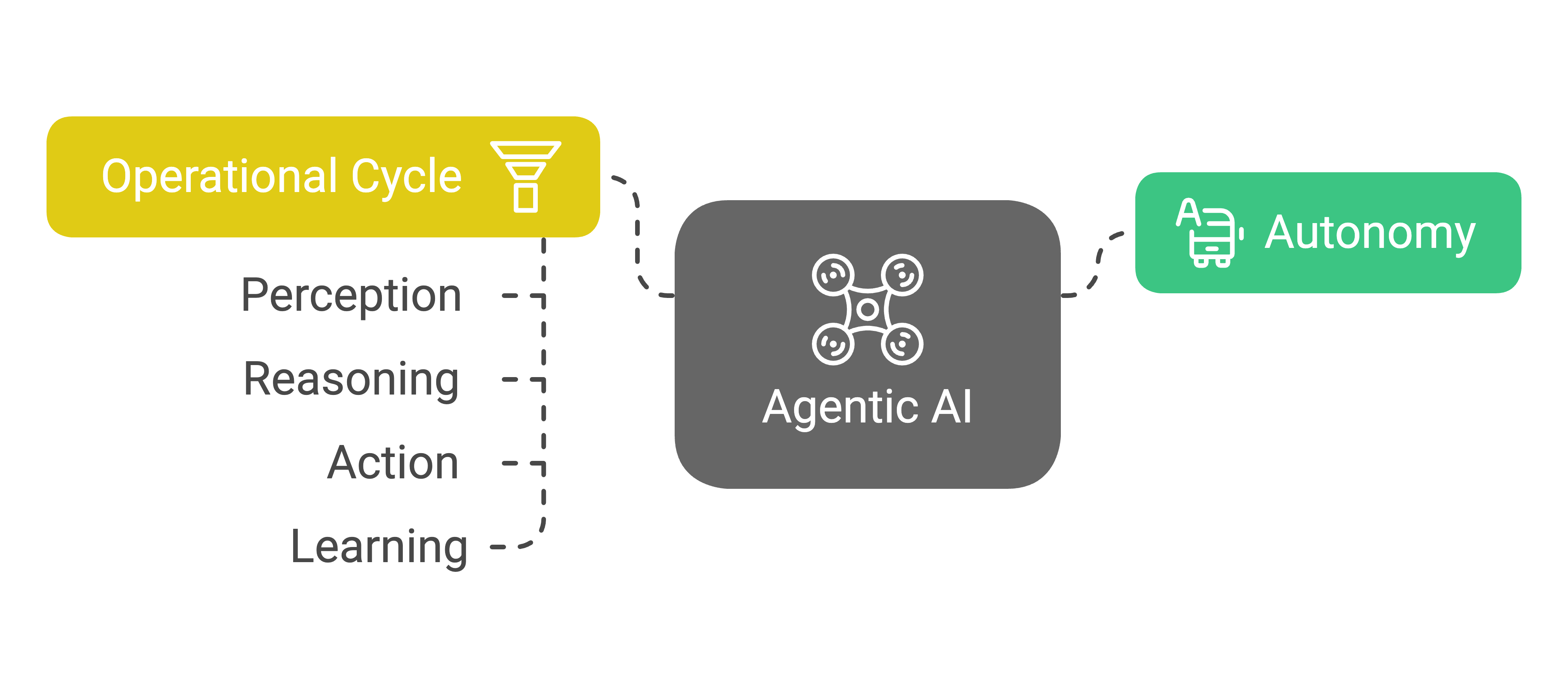
Agentic AI: The Autonomous Thinker
Agentic AI is characterized by its autonomy. It’s designed to make decisions, take actions, and learn from its experiences to achieve a specific goal, operating without constant oversight. Think of it as an AI entity capable of independent thought and adaptation. Agentic AI typically operates in a cycle that involves:
- Perception: Gathering information from its environment.
- Reasoning: Analyzing and understanding the gathered data.
- Action: Choosing the best action based on the analysis.
- Learning: Adapting and improving from feedback and experience.
This inherent autonomy enables Agentic AI to handle complex, dynamic tasks that require problem-solving, reasoning, and adaptation.
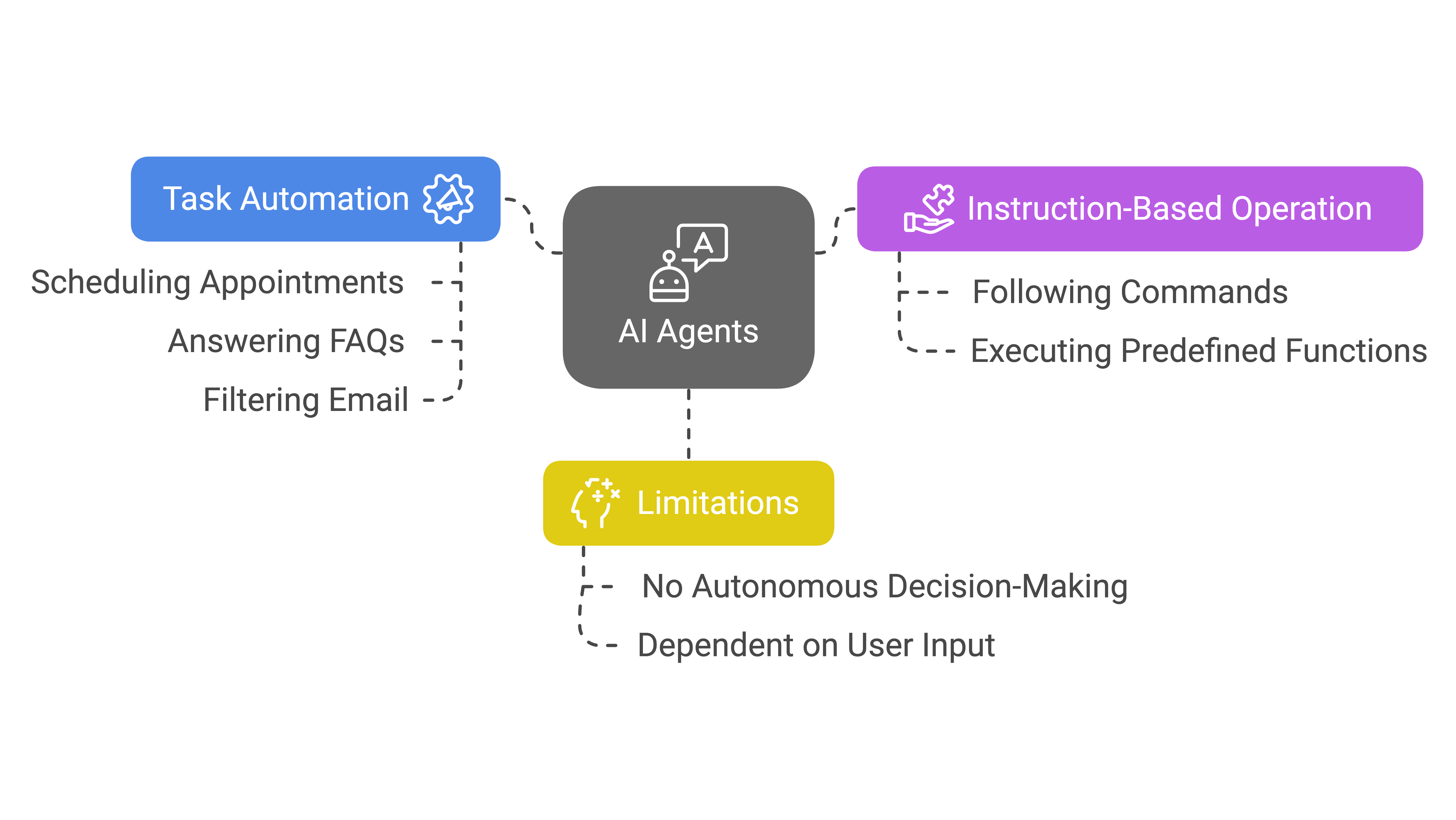
AI Agents: The Task-Oriented Helper
In contrast, AI Agents are generally designed to perform specific, defined tasks. They’re designed as virtual assistants that help with things like scheduling appointments, answering FAQs, or filtering email. AI Agents excel at automating routine tasks but lack the broader autonomous decision-making capabilities of Agentic AI. They operate on instructions rather than independent reasoning.
Key Differences: Autonomy vs. Task-Specific
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between AI Agents and Agentic AI:
| Feature | AI Agent | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Low; task-specific | High; operates independently |
| Decision-Making | Follows pre-programmed rules | Makes decisions based on reasoning |
| Learning | Learns to improve on the task but is not capable of independent and complex learning. | Learns and adapts continuously |
| Complexity | Handles simple, repetitive tasks | Handles complex, adaptive tasks |
| Primary Goal | Task Automation | Autonomous Goal Achievement |
Real-World Applications: Where Do They Fit?
Both AI Agents and Agentic AI are rapidly transforming how businesses and individuals operate. Let’s look at where each shines.
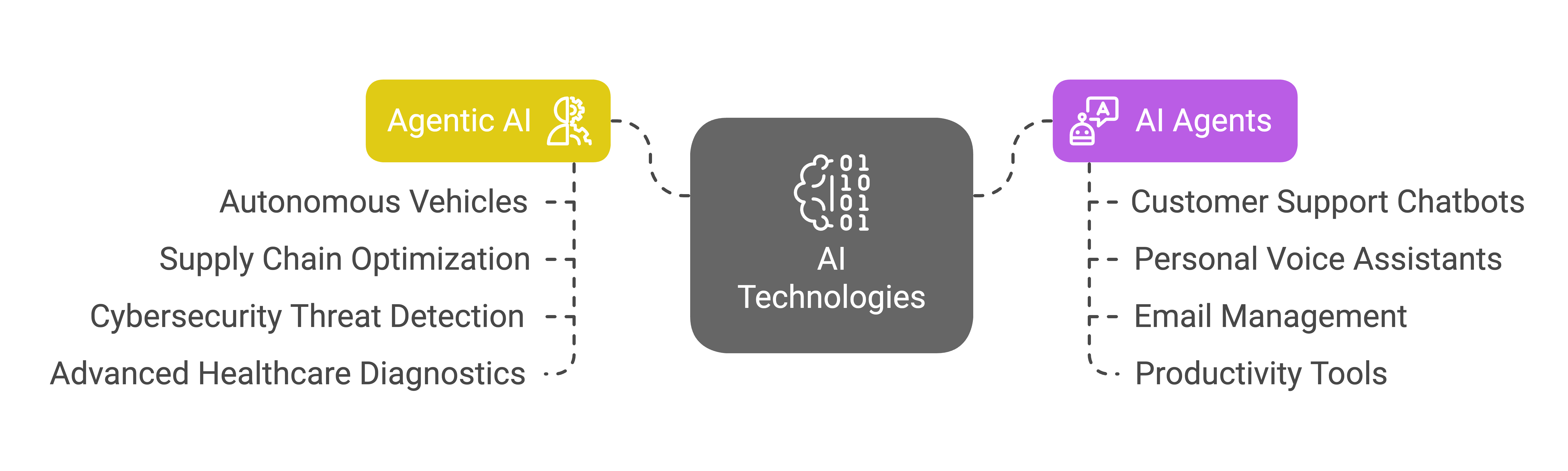
Agentic AI in Action:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use Agentic AI to navigate, make driving decisions, and adapt to changing road conditions. Tesla’s Full Self-Driving is a prime example, continuously learning from driving experiences.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Agentic AI manages inventory, predicts demand, and adjusts delivery routes autonomously, creating efficient supply chains. Amazon’s warehouse robots showcase this capability.
- Cybersecurity Threat Detection: Agentic AI systems identify and respond to cyber threats in real time by detecting anomalies in network activity. Darktrace is a notable example of a company using this approach.
- Advanced Healthcare Diagnostics: Agentic AI analyzes large datasets to assist with diagnosis, treatment recommendations, and patient care, like IBM Watson Health.
AI Agents in Action:
- Customer Support Chatbots: AI agents provide quick answers to common customer queries and resolve basic issues in real-time, such as those offered by Zendesk.
- Personal Voice Assistants: Assistants like Siri and Google Assistant manage tasks like scheduling, reminders, and playing music.
- Email Management: AI agents can sort emails, flag important messages, and provide smart replies, such as Google’s Smart Compose.
- Productivity Tools: AI agents can generate and debug code for developers, such as GitHub Copilot, enhancing productivity by suggesting code and helping with debugging.
The Future of AI Agents and Agentic AI
Future-of-AI-Agents-Agentic AI.webp Both paradigms offer incredible benefits but also pose challenges.
The Benefits
- Revolutionizing Industries: From autonomous vehicles to enhanced customer support, AI is making industries more efficient and cost-effective.
- Improved Decision-Making: Agentic AI can analyze vast amounts of data to make informed decisions often more accurately than humans.
- Personalization: AI can tailor services to individual needs and preferences, providing highly customized advice and solutions, particularly in areas like finance and healthcare.
The Challenges
- Job Displacement: The automation potential of AI raises concerns about potential job losses, although it also creates new types of opportunities.
- Ethical Concerns and Accountability: As AI becomes more autonomous, critical questions about accountability arise if the AI system makes an error.
- Data Privacy and Security: With AI systems handling vast amount of data, protecting user privacy becomes paramount.
Bridging the Gap
As AI evolves, the lines between these two paradigms are likely to blur. Imagine an AI Agent that can learn and adapt with the capabilities of Agentic AI. Such a combination could lead to even more powerful systems capable of handling complex automation needs and decisions.
Conclusion
AI Agents and Agentic AI represent two distinct but powerful approaches to artificial intelligence. While AI Agents excel at automating specific tasks, Agentic AI pioneers decision-making and autonomous learning. Understanding their differences is key to appreciating the evolving landscape of AI and harnessing its capabilities for the future. Both paradigms are essential for shaping our technological future, and by understanding them, we can leverage their strengths to improve the way we live and work.